
1. The Heart of Your Headphones
In the vast and exciting world of audio, it’s easy to get caught up in flashy brand names, luxurious materials, or a long list of smart features. However, beneath the surface of every headphone lies its true “engine” – the Headphone Drivers. This unsung hero is the core component responsible for transforming abstract electrical signals from your music player into the rich, tangible sounds that fill your ears. Without a capable driver, even the most beautifully designed headphones would remain silent.
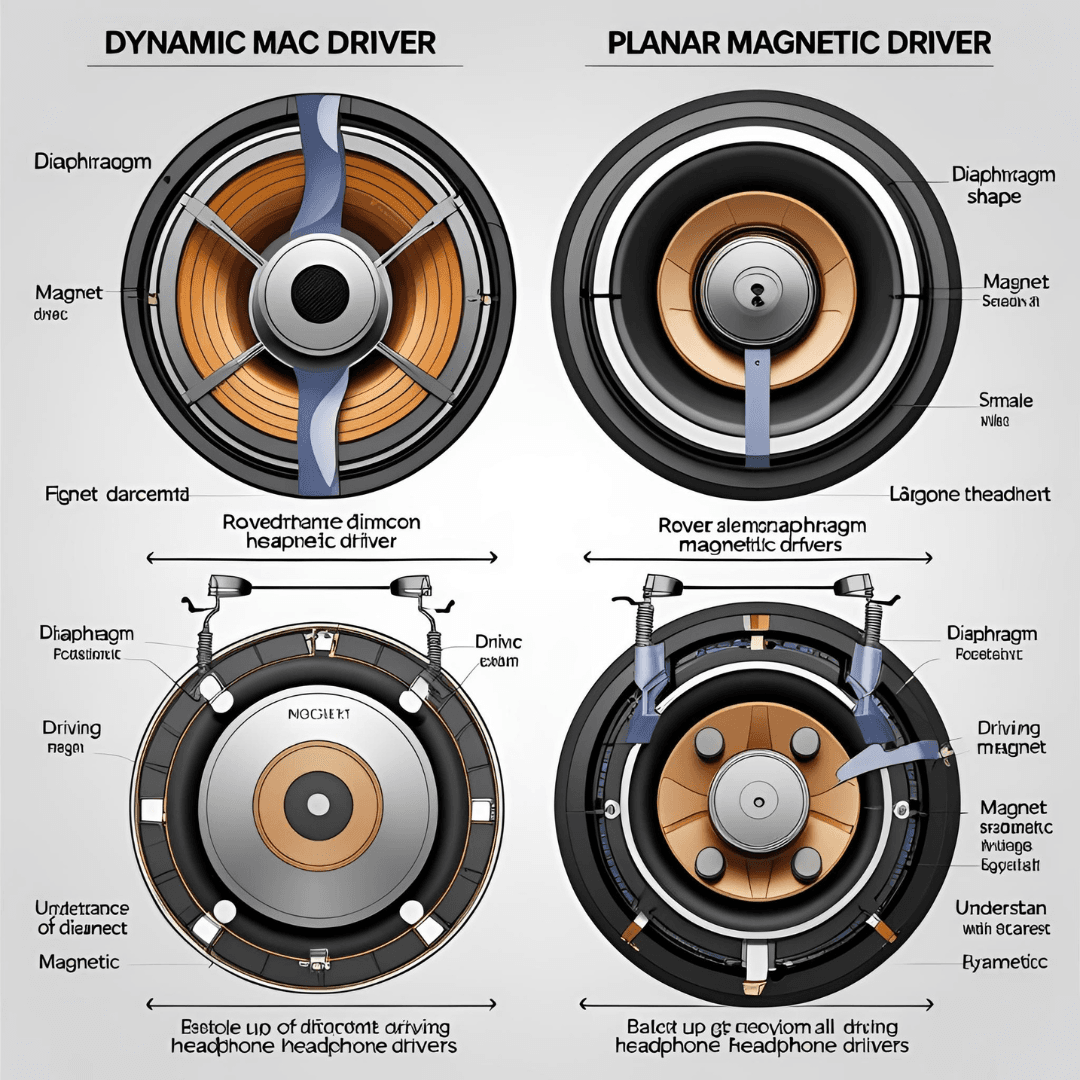
Among the myriad of driver technologies, Dynamic and Planar Magnetic stand out as the two dominant forces, especially in the realm of high-fidelity headphones. While both serve the same fundamental purpose of creating sound, they achieve it through distinct mechanical principles, leading to uniquely different listening experiences. This guide aims to demystify these complex workings, explaining how each driver type produces sound and, crucially, why these differences result in characteristic sound profiles. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of what goes on inside your headphones, empowering you to make a more informed choice for your next sonic adventure.

This guide will cover:
- What exactly a headphone driver is.
- The inner workings of dynamic drivers and their signature sound.
- The intricate mechanics of planar magnetic drivers and their distinct sonic characteristics.
- A direct, side-by-side comparison of their pros and cons to help you decide which technology aligns best with your listening preferences.
2. The Basics: What is a Headphone Driver?
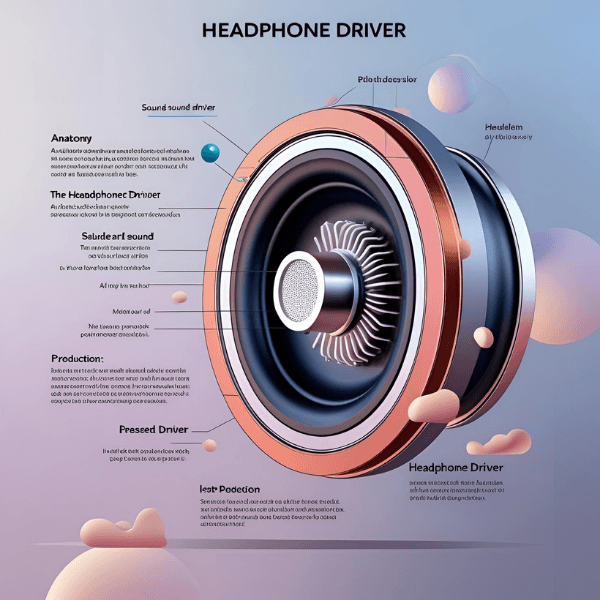
Before diving into the specifics of different driver types, it’s essential to understand the fundamental role a driver plays. Simply put, a headphone driver is the transducer—the component responsible for converting one form of energy into another. In this case, it takes electrical audio signals from your source (like your phone, digital audio player, or audio interface) and transforms them into mechanical vibrations. These vibrations then displace the air around them, creating the sound waves that travel to your ears, allowing you to hear music, podcasts, or game audio.
Think of it as a tiny, highly specialized loudspeaker built directly into your headphones. While their exact configurations vary, most drivers share a few core components that enable this transformation:
- Diaphragm: This is a thin, lightweight membrane that vibrates. It’s the part that physically moves to push the air and create sound.
- Magnet(s): These create a magnetic field, which is crucial for interacting with the electrical signal.
- Voice Coil / Conductors: These are wires that carry the electrical audio signal. They interact with the magnetic field to cause the diaphragm to move.
These elements work in concert to accurately reproduce the nuances of your audio, making the driver the most critical component influencing a headphone’s overall sound quality.
3. Dynamic Drivers: The Reliable Veteran

The dynamic driver is, by far, the most common type of headphone driver found today. Its design has been around for decades, proving itself as a robust, versatile, and highly effective way to produce sound. Think of it as a miniaturized version of the loudspeakers you see in a stereo system.
How They Work (Simplified):
At its core, a dynamic driver operates on a straightforward electromagnetic principle:
- Diaphragm: This is a thin, usually cone-shaped or dome-shaped, flexible membrane made from materials like Mylar, paper, or various plastics. It’s the part that actually moves the air to create sound waves.
- Voice Coil: A tiny coil of very fine wire is precisely attached to the center or edge of the diaphragm.
- Permanent Magnet: Surrounding the voice coil and diaphragm assembly is a stationary permanent magnet.
When an electrical audio signal from your music source flows through the voice coil, it generates a temporary electromagnetic field. This magnetic field then interacts with the fixed field of the permanent magnet. The resulting push and pull forces cause the voice coil (and, critically, the diaphragm it’s attached to) to move rapidly back and forth, vibrating in sync with the audio signal. These vibrations displace the air, creating the sound that reaches your ears.
Key Characteristics & Sound Profile:

Dynamic drivers are renowned for a distinct set of sonic traits that make them popular across a vast range of headphones:
- Punchy Bass: One of their most celebrated characteristics is their ability to deliver impactful, resonant, and often deep bass. This makes them a favorite for genres like electronic, hip-hop, rock, and pop.
- Warm & Engaging Sound: Many listeners describe dynamic headphones as having a “warm,” “organic,” or “full-bodied” sound signature. This often translates to a more musical and less analytical presentation, making for a very enjoyable listening experience.
- Efficiency: Generally, dynamic drivers are more efficient than other types, meaning they can achieve considerable volume levels with less power. This makes them highly suitable for use with portable devices like smartphones and basic digital audio players (DAPs) without needing an external amplifier.
- Cost-Effective: Due to their relatively simpler design and widespread manufacturing scale, dynamic drivers are typically more affordable to produce. This allows manufacturers to offer high-quality dynamic headphones across various price points, from budget-friendly to high-end.
- Versatility: You’ll find dynamic drivers in almost every type of headphone, including in-ear monitors (IEMs), on-ear, and over-ear headphones. They can be designed for both closed-back (offering good sound isolation) and open-back (providing a more spacious and natural soundstage) designs.
Common Applications:
Dynamic drivers are ubiquitous. They are widely used in everything from basic earbuds that come with your phone to professional studio monitoring headphones and high-end audiophile sets. Their robust nature and reliable performance make them a go-to choice for almost any listening scenario.
Popular Examples:
Iconic headphones like the Sennheiser HD 600 series (known for natural, detailed sound) and the Beyerdynamic DT series (revered for their durability and clear, analytical sound) are prime examples of excellent dynamic driver implementations.
4. Planar Magnetic Drivers: The Detail & Precision Maestro

Stepping into a more specialized realm, planar magnetic drivers represent a distinct and highly regarded approach to headphone sound reproduction. While less common than dynamic drivers, they are celebrated in audiophile circles for their unique sonic properties, particularly their precision and detail.
How They Work (Simplified):
Unlike the coil-and-cone setup of dynamic drivers, planar magnetic drivers operate on a principle that distributes force more evenly across the sound-producing surface:
- Ultra-Thin, Flat Diaphragm: This is the heart of the planar magnetic driver. Instead of a cone, it’s a very thin, flat, and lightweight membrane (often made from materials like Mylar or Kapton). Crucially, the conductive traces (the equivalent of a voice coil) are directly etched or embedded onto the surface of this diaphragm, covering a significant portion of its area.
- Planar Magnets: Arrays of permanent magnets are precisely positioned on both sides of the flat diaphragm, creating a uniform and powerful magnetic field that spans its entire surface.
When an electrical audio signal flows through the conductive traces on the diaphragm, it creates an electromagnetic force. Because this force is distributed evenly across the large, flat surface of the diaphragm (rather than concentrated at a single voice coil point), the entire diaphragm moves in a unified, piston-like motion. This highly controlled and precise movement of air is what translates into the planar magnetic’s distinctive sound.

Key Characteristics & Sound Profile:
Planar magnetic headphones are known for a specific set of sonic traits that audiophiles often seek out:
- Exceptional Detail & Clarity: This is perhaps their most celebrated attribute. Planar magnetic drivers are renowned for their incredible resolution, allowing listeners to discern minute details, subtle textures, and layers in music that might be missed on less resolving drivers.
- Fast, Controlled Bass: Unlike the punchier, sometimes more resonant bass of dynamic drivers, planar magnetic bass is often described as “tight,” “articulate,” and “textured.” It’s incredibly precise, starting and stopping quickly, providing a highly accurate representation of low frequencies rather than just a booming impact.
- Expansive Soundstage & Imaging: Due to the large, flat diaphragm’s ability to move air uniformly, planar magnetics naturally create a wide, open, and precise soundstage. Instruments are typically well-separated and can be clearly “placed” within a three-dimensional soundscape, offering an immersive listening experience.
- Low Distortion: Because the driving force is spread uniformly across the diaphragm’s surface, planar magnetic drivers typically exhibit very low harmonic and intermodulation distortion, even at higher listening volumes. This contributes to their clean and uncolored sound.
- Lower Efficiency (Generally): Planar magnetic drivers often require more power to reach optimal listening volumes compared to dynamic drivers. This means they usually benefit significantly from a dedicated headphone amplifier (amp), which can add to the overall cost but unlocks their full sonic potential.
- Higher Cost: The more complex manufacturing process, the precision required, and the often larger number of high-strength magnets contribute to a generally higher price point for planar magnetic headphones.
Common Applications:
While dynamic drivers are found across the spectrum, planar magnetic drivers are predominantly featured in open-back, audiophile-grade over-ear headphones. Their design lends itself well to larger form factors, allowing for the extensive magnet arrays and larger diaphragms that contribute to their signature sound. They are highly favored for critical listening, mixing, and mastering due to their accuracy.
Popular Examples:
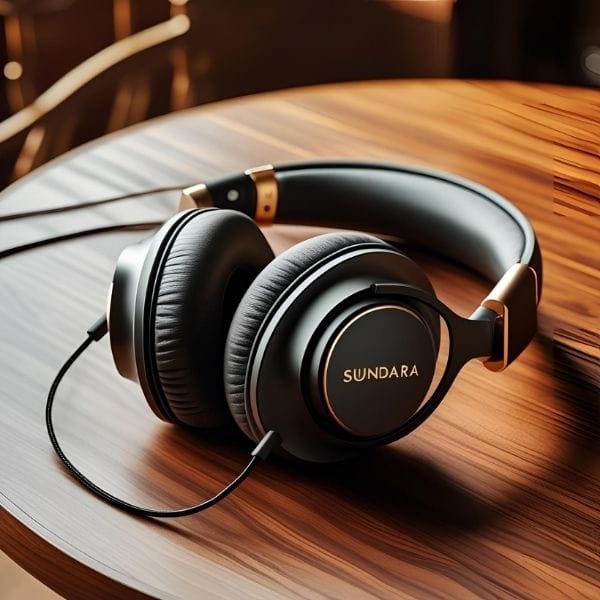

Companies like Hifiman have been instrumental in making planar magnetic technology more accessible with models like the Sundara and HE400se. At the higher end, Audeze‘s LCD series are widely considered benchmarks for planar magnetic performance.
5. Dynamic vs. Planar Magnetic: A Side-by-Side Comparison

When it comes down to making a choice, understanding the direct trade-offs between dynamic and planar magnetic drivers is crucial. While both aim to deliver an immersive audio experience, they do so through different methodologies, resulting in distinct sonic signatures and practical considerations.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison to help clarify their differences:
In-Depth Breakdown of Key Differences:
- Working Principle: This is the core differentiator. Dynamic drivers use a single voice coil attached to the center of a cone-shaped diaphragm, moving it like a piston. This concentrated force can lead to slight flexing of the diaphragm, especially at higher volumes. Planar magnetic drivers employ a flat diaphragm with conductive traces evenly distributed, moved by a uniform magnetic field from arrays of magnets on either side. This even force distribution results in a more cohesive and precise movement of the entire diaphragm.
- Bass Response: Dynamic drivers are often lauded for their punchy, impactful, and resonant bass. This makes them feel more “fun” for many listeners and excels with genres that benefit from a strong low-end presence like EDM, hip-hop, and pop. Planar magnetic drivers, conversely, deliver bass that is typically described as fast, tight, and highly controlled. It’s less about raw impact and more about texture and articulation, allowing you to hear the individual notes of a bassline with impressive clarity.
- Detail & Clarity: This is where planar magnetics often claim superiority. Their uniform diaphragm movement and low distortion allow them to retrieve exceptional micro-details and textures within a recording that might be less apparent with dynamic drivers. Dynamic drivers are still “good” in detail, but can sometimes present a slightly less analytical or “smoother” sound.
- Soundstage: The sense of space and instrument separation, known as soundstage, is often a strong suit for planar magnetic headphones. Their design naturally lends itself to creating a wider, more open, and precise soundstage, allowing instruments to breathe and be distinctly placed within the stereo image. While many dynamic headphones also offer good soundstages, it’s a consistent strength for planar magnetic designs.
- Distortion: Due to the even force distribution across their diaphragm, planar magnetic drivers generally exhibit very low levels of distortion, even when pushed to higher volumes. This contributes to their clean and accurate sound. Dynamic drivers, particularly at their volume limits, can sometimes introduce higher levels of distortion as the single voice coil might flex the diaphragm unevenly.
- Efficiency: Dynamic drivers are typically more efficient, meaning they can be driven to sufficient listening volumes with less power. This makes them ideal for direct connection to smartphones, laptops, or portable digital audio players without the need for additional amplification. Planar magnetic drivers are generally less efficient and often benefit significantly from a dedicated headphone amplifier (amp) to unlock their full dynamic range and achieve optimal performance.
- Cost: The manufacturing process for dynamic drivers is more established and less complex, leading to a wider range of affordable options that still offer excellent sound quality. Planar magnetic headphones tend to be more expensive due to the precision required in their construction and the cost of the magnet arrays.
- Weight: As a consequence of the magnet arrays on both sides of the diaphragm, planar magnetic headphones are often heavier than their dynamic counterparts. This can be a factor for long listening sessions.
- Ideal For: Dynamic headphones are perfect for general listening, portable use, and anyone who prefers an impactful, engaging bass response. Planar magnetic headphones are a favorite among audiophiles, professionals for critical listening and mixing, and those who prioritize unrivaled detail retrieval and a spacious soundstage.
6. Choosing Your Sonic Signature

As we’ve explored the fascinating world of headphone drivers, it becomes clear that the choice between dynamic and planar magnetic technologies isn’t about finding a definitive “winner.” Instead, it’s about understanding their unique strengths and weaknesses, recognizing that neither is inherently “better,” but rather different, each offering a distinct sonic signature.
Dynamic drivers, the reliable veterans, continue to impress with their impactful bass, warm character, and excellent efficiency, making them a superb choice for everyday listening, portable use, and those who enjoy a more energetic sound. Planar magnetic drivers, the precision maestros, excel in delivering unparalleled detail, tight and articulate bass, and expansive soundstages, appealing to critical listeners and audiophiles who crave sonic transparency.
Ultimately, the “best” driver type for you hinges entirely on your personal listening preferences, your primary use case, and your existing audio setup. Do you prioritize ease of use and punchy bass for on-the-go listening, or are you seeking surgical detail and a vast soundstage for dedicated sessions at your desk? Do you already own or plan to invest in a dedicated headphone amplifier, which can unlock the full potential of less efficient planar magnetic headphones?
We encourage you to consider your priorities. Do you value the punchy bass and efficiency of dynamic drivers, or are you drawn to the surgical detail and expansive soundstage that planar magnetic drivers offer? By aligning your sonic preferences with the strengths of each driver type, you can make an informed decision that elevates your listening experience.
Understanding your headphone’s engine is the first step to truly appreciating the sound it delivers. So, go forth, explore, and find the driver that resonates with your ears and fuels your passion for great audio.


k3y6zt
Pingback: What's The Difference Between Open-Back And Closed-Back Headphones?
Pingback: Revolutionary Next-Gen Wireless Earbuds: Transform How You Listen & Live (2025)
Pingback: High-Resolution Audio Streaming: Is The Upgrade Worth It In 2025?
Pingback: Best Hi-Res Audio Gear 2025: Top DACs, Amps & Headphones For Audiophiles
Pingback: Get The Best Sound From Your Bluetooth Speaker: 7 Pro Tips For 2025
Pingback: Affordable Hi-Fi Headphones 2025: Top Picks Under $200 For Audiophile Sound